In today’s rapidly evolving industrial and agricultural landscapes, precision, automation, and efficiency are more critical than ever. Mobile Machine Control Systems (MMCS) are at the forefront of this transformation, integrating advanced electronics, sensors, software, and connectivity to enable smart, autonomous, and semi-autonomous mobile machinery. From construction and mining to agriculture and logistics, MMCS are redefining how heavy-duty mobile machines operate, optimizing performance while reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
What is a Mobile Machine Control System?
A Mobile Machine Control System is a sophisticated platform that manages and automates the movement and functions of mobile machinery. These systems typically incorporate:
Sensors (GPS, IMUs, encoders) for position and motion detection
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) for logic and communication
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) for user interaction
Wireless communication modules for remote access and data exchange
Control algorithms and embedded software for intelligent decision-making
By integrating these elements, MMCS ensure accurate control over complex machine functions such as navigation, steering, digging, lifting, plowing, or harvesting—based on real-time inputs and pre-configured tasks.
Core Components of a Mobile Machine Control System
Embedded Control Software
Custom algorithms handle real-time inputs from sensors and make control decisions accordingly.
Software is often developed using model-based design tools like MATLAB/Simulink.
GPS and GNSS Technologies
Offer high-precision location tracking (often centimeter-level) for navigation and operation.
Essential in applications like automated agriculture, where path accuracy is critical.
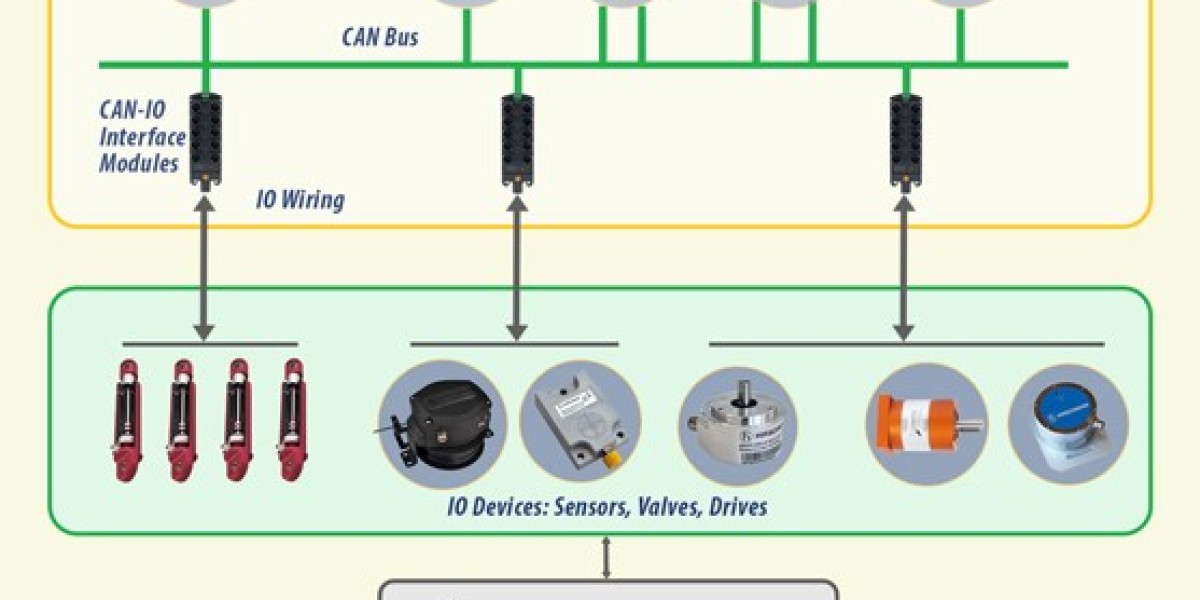
Sensors and Actuators
Accelerometers, gyroscopes, pressure sensors, and load cells provide real-time data.
Actuators respond with appropriate mechanical movements—enabling full machine automation.
Control Units and CAN Bus Communication
ECUs act as the brain of the system, processing sensor data and sending commands to actuators.
Communication between components is typically handled via CAN (Controller Area Network) protocols.
User Interfaces and Displays
Touchscreens, joysticks, and dashboards allow operators to interact with the system.
Advanced UIs provide diagnostics, system status, and allow for parameter tuning.
Applications Across Industries
? Agriculture
Mobile Machine Control Systems are transforming farming through precision agriculture. Automated tractors and harvesters equipped with MMCS can follow GPS-guided paths, apply fertilizers accurately, and monitor crop conditions—all with minimal human input.
?️ Construction
In construction, MMCS are used in excavators, graders, and bulldozers. Systems ensure precise leveling, depth control, and automated digging operations. They reduce rework, improve productivity, and enable remote operation in hazardous zones.
⛏️ Mining
Mining vehicles such as haul trucks and loaders benefit from semi-autonomous control, enhancing safety in harsh environments. MMCS improve route efficiency, reduce idle times, and facilitate fleet management.
? Material Handling and Logistics
Autonomous forklifts and AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) use MMCS for real-time navigation and inventory movement, streamlining warehouse operations and reducing manual labor.
Advantages of Mobile Machine Control Systems
✅ Increased Productivity
Automated and semi-autonomous functions reduce operator fatigue and increase operational speed and accuracy, leading to significant productivity gains.
✅ Improved Accuracy and Precision
With GPS and sensor integration, machines can perform repetitive tasks with pinpoint accuracy, minimizing errors and material waste.
✅ Lower Operating Costs
By reducing fuel usage, operator time, and material wastage, MMCS contribute to lower total cost of ownership.
✅ Enhanced Safety
Remote operation and intelligent control reduce human exposure to hazardous environments, enhancing workplace safety.
✅ Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Telematics integration allows for data collection, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance, ensuring machines run efficiently with minimal downtime.
Challenges and Considerations
While MMCS offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges that must be addressed:
System Integration: Combining mechanical, electrical, and software components requires cross-disciplinary expertise.
Data Security: As machines become more connected, ensuring cybersecurity is crucial.
Initial Investment: High upfront costs can be a barrier for small and medium enterprises.
User Training: Operators must be trained to interact with automated systems effectively.
The Role of Model-Based Design in MMCS
Model-based design (MBD) plays a pivotal role in MMCS development. It allows engineers to simulate and test control algorithms using digital twins before implementation. Tools like Simulink enable early validation, reduce development cycles, and ensure reliability in real-world deployment.
With MBD, teams can:
Test control logic virtually
Generate auto-code for ECUs
Validate safety-critical scenarios
Reduce prototyping costs and time-to-market
The Future of Mobile Machine Control Systems
With rapid advancements in AI, IoT, and edge computing, the next generation of MMCS will be even more intelligent and connected. Expect to see:
Full autonomy with real-time decision-making based on AI algorithms
Swarm robotics in agriculture and construction for coordinated tasks
Cloud connectivity for real-time diagnostics and software updates
Sustainability tracking, measuring emissions and energy consumption per task
MMCS will continue to play a central role in Industry 4.0 initiatives, enabling businesses to automate operations, enhance sustainability, and stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion
Mobile Machine Control Systems by Servotechinc represent a leap forward in intelligent automation for mobile equipment. From precision agriculture to autonomous construction vehicles, MMCS enable greater efficiency, accuracy, and control in demanding environments. As technology evolves, businesses that adopt MMCS early will gain a competitive edge through reduced operational costs, enhanced productivity, and improved safety. Investing in these systems isn’t just about automation—it’s about smarter, safer, and more sustainable operations.